Project-Based Learning (PBL) has moved past buzzword status to become a pivotal link between traditional classroom instruction and the essential skills demanded by the modern age. This pedagogical movement responds to the needs of both students and teachers in real time, shifting education to more closely resemble the world outside the classroom. PBL empowers students to navigate their learning journey by aligning academic milestones with personal passions and real-world issues. PBL often places learning in the real world: students engage with experts in various fields and apply their knowledge in tangible ways.
Unlike conventional approaches that often culminate in standardised assessments, PBL places the emphasis on the learning process itself. Imagine a student grappling with the question, "How can I create my own movie?" This question acts as a frame for acquiring skills: editing, camera work, directing, and writing. Rather than being passive listeners, students actively pursue what they need to achieve their filmmaking aspirations.
Two architects of innovation in education, Elyse Klaidman, Co-Founder of Story Xperiential, and Felipe Prado, Co-Founder of Swarmob, shed light on the essence of creating a PBL environment that engages students in driving their own learning.
Making space for diverse student interests in a single classroom is a complex challenge, but PBL’s versatile approach can be tailored to specific subjects while preserving the ethos of self-directed learning. One group leading the way is Story Xperiential, an initiative by X in a Box designed to cultivate specialised project-based learning. Using narrative animation as a hook, Story Xperiential invites students to dive head-first into the art of crafting stories.
Guided by both industry experts and fellow students, this program brings together theory and practice, creating an environment that is both vibrant and engaging. Through its PBL method, Elyse Kleidman envisions a future where projects serve to develop skills and expose students to a range of specialised career prospects.
However, incorporating new and open-ended learning does not come without its challenges. While PBL holds immense promise, its implementations demand significant investment from educators and schools alike to get the program rolling. Finding a balance between student autonomy and program coherence can be overwhelming, especially when it comes down to tracking each individual student's work, how to assess them and continue challenging them to grow. Chile-based Swarmob has identified this problem and has developed an online application for use throughout Latin America that allows for easy management. With a focus on PBL integration and providing a platform for managing student work and goal setting, Swarmob equips students with tools for solving social and environmental problems collaboratively.
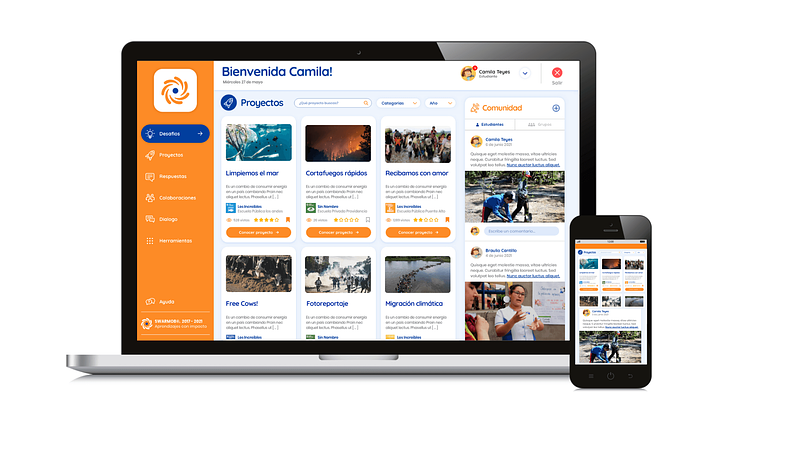
Swarmob aims to make integration of PBL smooth and approachable by providing a comprehensive network that allows educators to assign tasks, create learning paths, organise learning materials, and conduct formative assessments. By lowering barriers to entry, this framework helps administrations adopt PBL in their schools. Furthermore, they have integrated a system that connects other schools that implement PBL learning and provide connections to industry experts.
Project-Based Learning’s rapid growth has seen it implemented across the education sector. It is a methodology that dives deeper into learning, allowing the students to find their own purpose within their studies. Story Xperiential and Swarmob are two examples of how careful management, guidance, and lessons enrich the experience. But change does not need to mean redesigning the entire curriculum of a school - it can be taken in small steps on a class to class basis.
If you have an innovation working on PBL we would love to hear from you! Register at HundrED and apply for the 2025 Global Collection!



