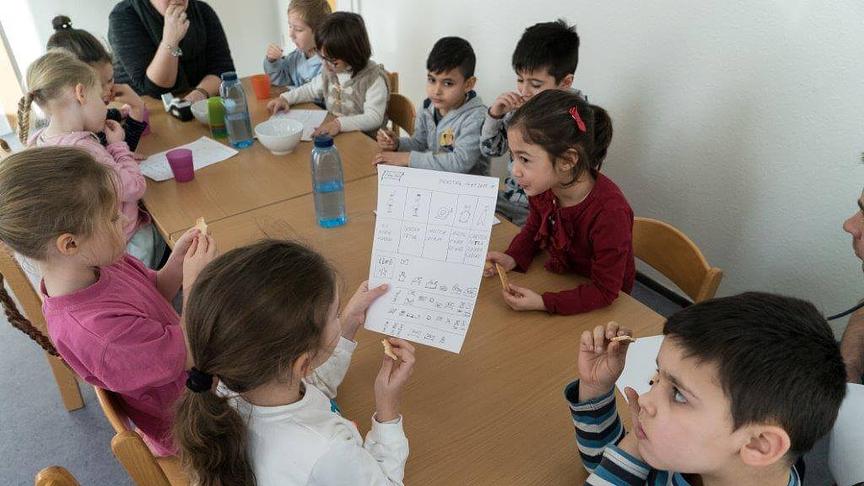
Democracy in Kindergartens is a nationwide pilot project that aims to bring democratic decision-making to German kindergartens.
The rights of children, as set out in the UN Convention on Childrens’ Rights, is implemented in allkindergartens through the project. For the safeguarding and protection of childrens’ rights, all kindergartens practice democratic processes with the children. They examine these as a groupand each individual kindergarten can verify their own democratic development through a certification process.
In a Democratic Kindergarten, the constitution is shaped by the children, with teachers transferring rights to children in an age-appropriate way. The specially trained teachers are equipped to distinguish between opportunities for children to wholly or partially make a decision on something,and to specify when there are times when the educators should take the lead. The focus is on the democratic process itself, not just the vote.
The constitution of the kindergarten is an open framework and is constantly changing through participation. Every new decision is made in this way, as a rolling process. Rules are discussed, negotiated and agreed by all participants to ensure they make sense and are fair. Through this process, children learn from a young age that the commonly agreed rules are mandatory for everyone. This reliability and fairness gives children a framework for their expected behaviour at kindergarten.
The approach also teaches young children that they won’t always get their own way, and that there are different opinions and ideas that are also valid and need to be accepted. This is a major learning objective and the hope is that children will learn to be valuable members of a democracy,tolerant of others and always searching for peaceful solutions. The main challenges are for the staff to share power and to monitor and lead complex discussions to reach a consensus. The parents are completely involved in and informed about the project.